The primary functions of RBI are to control the supply of money in the economy and also ‘the cost of credit.’ Meaning, how much money is available for the industry or the economy and what is the price that the economy has to pay to borrow that money. ‘Availability of money’ is nothing but liquidity and ‘cost of borrowing’ is interest rates.
These two things (Supply of money and cost of credit) are closely monitored and controlled by RBI. The inflation and growth in the economy are primarily impacted by these two factors.
To control inflation and the growth, RBI uses certain tools like Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR), Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR), Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate etc.,

Almost every investor would have heard about the term repo rate in their financial life journey. However, not many investors are actually aware of what this term means and why it is so important.
“The repo rate market is often referred to as the beating heart of the money market.”
In this post, let’s understand – What is the meaning of Repo Rate? What is the importance of Repo rate and how the repo market influences the larger economy?
What is Repo Rate?
When we need money, we take loans from banks. And banks charge certain interest rate on these loans. This is called as cost of credit (the rate at which we borrow the money).
Similarly, when banks need money they approach RBI. The rate at which banks borrow money from the RBI by selling their surplus government securities to the central bank (RBI) is known as “Repo Rate.” Repo rate is short form of Repurchase Rate. Generally, these loans are for short durations (up to 2 weeks).
It simply means the rate at which RBI lends money to commercial banks against the pledge of government securities whenever the banks are in need of funds to meet their day-to-day obligations.
Banks enter into an agreement with the RBI to repurchase the same pledged government securities at a future date at a pre-determined price. RBI manages this repo rate which is the cost of credit for the bank.
Example – If repo rate is 6.5%, and bank takes loan of Rs 1000 from RBI, they will pay interest of Rs 65 to RBI.
Through Repo rate market RBI tries to inject cash into the market by buying securities on collateral from the banking institutions . On the other hand, sometimes they also sell securities in order to suck out the additional cash from the system. This is known as a reverse repo.
Impact of Repo Rate on a Common Man | Importance of Repo rate
Higher the repo rate, higher the cost of short-term money and vice versa. Higher repo rate may slowdown the growth of the economy. If the repo rate is low then banks can charge lower interest rates on the loans taken by us.

So, what is the actual link between the repo rate and your loans like home loan?
The banks offer/charge certain ‘rate of interest’ on deposits and loans. The rate of interest charged by a financial institution for lending money is known as ‘Lending Rate‘.
The method to arrive at Lending Rate has changed drastically over the last decade or so. Banks & Financial Institutions have been using the below Lending Rates;
- BPLR (Benchmark Prime Lending Rate)
- Base Rate (Base Rate replaced BPLR w.e.f July, 2010)
- MCLR – Marginal Cost of Fund based Lending Rate (MCLR has been in effect since April 1, 2016.)
- RLLR – Repo Linked Lending Rate (available w.e.f 1st Jul, 2019)
If you visit any of the bank’s portal and check the applicable interest rates on home loans, you can find the rate of interest (lending rate) is now linked to the repo rate. Hence, any change in repo-rate, your EMIs on existing/new loans get affected.
The interest rate on every retail loan has two components – the benchmark rate i.e., repo-rate and the spread (margin). The spread is calculated based on the borrower’s credit score, income source, and loan size.
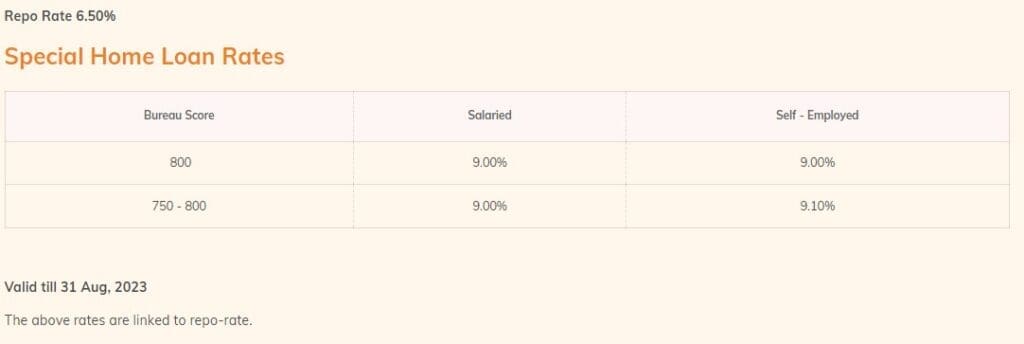
For example, if a salaried borrower has a credit score of 800, considered good, the interest spread can be say 2.50 over the repo rate. So, the final interest rate will be 6.50 + 2.50 = 9.00%.
Key points
- Repo rate is used as benchmark for setting interest rates on loans when there is high inflation, the RBI increases the repo rate so that commercial banks do not borrow money. This consequently reduces the liquidity in the market, controlling inflation.
- A decrease or increase in the repo rate impacts a variety of loans, such as gold loans, home loans, vehicle loans, and personal loans.
- Stock market and interest rates have an inverse relationship. Each time the repo rate experiences an increase, the stock markets get instantly impacted (negatively).
- An increase in repo rate could be beneficial for those looking for FDs with competitive rates and low risk.
Latest Repo Rate (10-Aug-2023) is 6.5%.
Continue reading:
- Latest Floating Rate Reset Rules on Loans | RBI’s Guidelines
- Important Macro Economic Indicators you need to track as an Investor!
- What is Negative Real Interest Rate? | How Can Interest Rates Be Negative?
- Who gets the Joint Bank Account Monies if one Account Holder dies?
- Income Tax Deductions List FY 2023-24 | Under Old & New Tax Regimes
(Post first published on : 10-Aug-2023)
